Health Expenditures in OECD & Turkey
Health Expenditure to GDP Ratio (%)10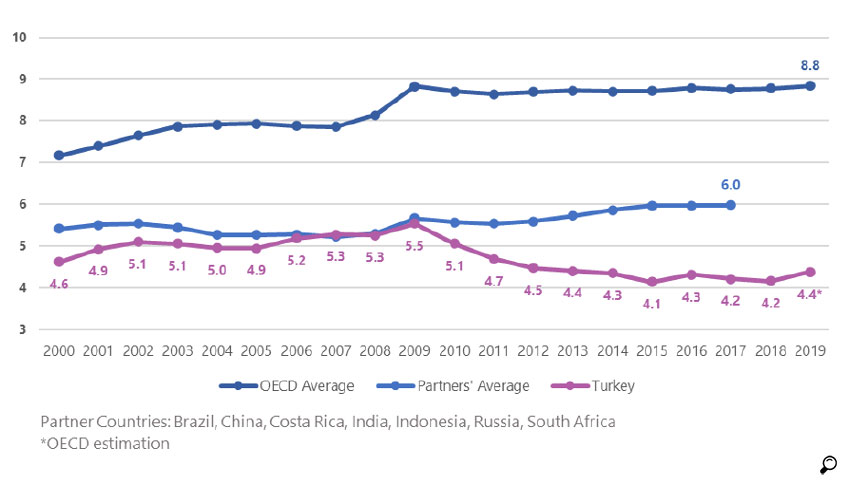
The decreases in the healthcare spending trend are also observed in pharmaceutical spending. Prior to 2008, before the introduction of Health Transformation Programme reforms, the ratio of the pharmaceutical budget to the national income was kept in the range of 1.3 - 1.4% of GDP while it increased to 1.7% of GDP in 2009 as a result of the 2008 economic crisis. In 2009, due to the economic contraction, health payments, which were among the salient expense items of the Institution, were examined closely and payments for pharmaceuticals were judged as a major budget item to be restricted. Medicines expenses of SSI were reduced to 0.8% of the GDP during 2015-2017, the share increased however steadily thereafter to reach to 0.9% of GDP in 2019.
Three instruments are used to control drug prices in Turkey:

